lv pcwp mitral stenosis | pcwp for pulmonary hypertension lv pcwp mitral stenosis In most cases, the PCWP is also an estimate of left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). The normal pulmonary capillary wedge . Flow is now a part of Allianz Insurance, check out our rebrand FAQs.
0 · pcwp pulmonary capillary wedge
1 · pcwp measurement cv
2 · pcwp for pulmonary hypertension
3 · pcwp for pulmonary edema
4 · mitral valve stenosis pcwp
5 · elevated pcwp levels
6 · cv physiology pcwp
7 · aortic valve stenosis cv
Richard Rogers I bought my LV LX new in 2010 and apart from a little road noise it has been great. Megan Edwards I bought the Focus because it was cheap and I could afford to pay cash for it. I have done 60,000km in it and I have not had any mechanical problems.
In practical use, valve area is used to assess the severity of aortic and mitral stenosis. No valve area for defining severe tricuspid valve stenosis is agreed on, and pulmonic stenosis is usually assessed with gradient alone. In most cases, the PCWP is also an estimate of left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). The normal pulmonary capillary wedge . In practical use, valve area is used to assess the severity of aortic and mitral stenosis. No valve area for defining severe tricuspid valve stenosis is agreed on, and pulmonic stenosis is usually assessed with gradient alone. In most cases, the PCWP is also an estimate of left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). The normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is between 4 to 12 mmHg. Elevated levels of PCWP might indicate severe left ventricular failure or severe mitral stenosis.
Uncommonly, mitral stenosis, pulmonary vein stenosis, or pulmonary veno-occlusive disease can also cause a higher PAWP than LVEDP. Obtaining an accurate PAWP is especially important because this has been shown to have prognostic significance greater than that of the LVEDP in certain subgroups of patients by measuring the effect of LA and LV .It is helpful to measure PCWP to diagnose the severity of left ventricular failure and to quantify the degree of mitral valve stenosis. Both conditions elevate LAP and, therefore, PCWP. Aortic valve stenosis and regurgitation, and mitral regurgitation also elevate LAP.
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF LV FILLING PRESSURES AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION GRADE. The key variables recommended for assessment of LV diastolic function grade include mitral flow velocities, mitral annular e0 ve-locity, E/e0 ratio, peak velocity of TR jet, and LA maximum volume index (Figure 8B). The cause of MR was myxomatous MVD in 6 patients, incomplete mitral leaflet closure with LV dilatation and depressed LVEF in 5 patients, and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy in 3 patients. The mean PCWP of the group was 21±8 mm Hg (range, 9 to 35).

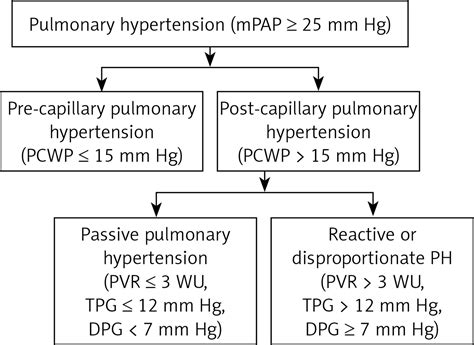
Conditions in which PAW does not approximate PCWP. UpToDate, electronic clinical resource tool for physicians and patients that provides information on Adult Primary Care and Internal Medicine, Allergy and Immunology, Cardiovascular Medicine, Emergency Medicine, Endocrinology and Diabetes, Family Medicine, Gastroenterology and Hepatology .Assessment of mitral stenosis using PAWP and LV pressures has been shown to be inaccurate . We herein present an easy and safe alternative method to the traditional transseptal approach for measurement of direct LA pressure in patients with mitral stenosis.Left-sided cardiovascular diseases include mitral and aortic valve disease, diastolic LV dysfunction, and systolic LV dysfunction. A hypertensive crisis with acute pulmonary edema in the presence of normal contractile function may be a sequela of .
We sought to evaluate the correlation between PCWP and LAP and to compare transmitral gradients obtained with LAP and PCWP in MS, before and after balloon mitral valvotomy (BMV). In practical use, valve area is used to assess the severity of aortic and mitral stenosis. No valve area for defining severe tricuspid valve stenosis is agreed on, and pulmonic stenosis is usually assessed with gradient alone. In most cases, the PCWP is also an estimate of left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP). The normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is between 4 to 12 mmHg. Elevated levels of PCWP might indicate severe left ventricular failure or severe mitral stenosis.
Uncommonly, mitral stenosis, pulmonary vein stenosis, or pulmonary veno-occlusive disease can also cause a higher PAWP than LVEDP. Obtaining an accurate PAWP is especially important because this has been shown to have prognostic significance greater than that of the LVEDP in certain subgroups of patients by measuring the effect of LA and LV .It is helpful to measure PCWP to diagnose the severity of left ventricular failure and to quantify the degree of mitral valve stenosis. Both conditions elevate LAP and, therefore, PCWP. Aortic valve stenosis and regurgitation, and mitral regurgitation also elevate LAP.
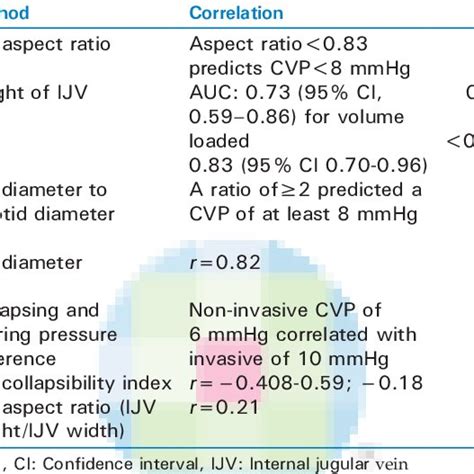
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF LV FILLING PRESSURES AND DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION GRADE. The key variables recommended for assessment of LV diastolic function grade include mitral flow velocities, mitral annular e0 ve-locity, E/e0 ratio, peak velocity of TR jet, and LA maximum volume index (Figure 8B).
The cause of MR was myxomatous MVD in 6 patients, incomplete mitral leaflet closure with LV dilatation and depressed LVEF in 5 patients, and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy in 3 patients. The mean PCWP of the group was 21±8 mm Hg (range, 9 to 35).Conditions in which PAW does not approximate PCWP. UpToDate, electronic clinical resource tool for physicians and patients that provides information on Adult Primary Care and Internal Medicine, Allergy and Immunology, Cardiovascular Medicine, Emergency Medicine, Endocrinology and Diabetes, Family Medicine, Gastroenterology and Hepatology .Assessment of mitral stenosis using PAWP and LV pressures has been shown to be inaccurate . We herein present an easy and safe alternative method to the traditional transseptal approach for measurement of direct LA pressure in patients with mitral stenosis.
pcwp pulmonary capillary wedge
Left-sided cardiovascular diseases include mitral and aortic valve disease, diastolic LV dysfunction, and systolic LV dysfunction. A hypertensive crisis with acute pulmonary edema in the presence of normal contractile function may be a sequela of .
pcwp measurement cv
Sazinies. Nosūtīt. Veiksmigi nosūtīts! Gribi: Sadarboties? Pasūtīt šovu? Mācīties "Flow arts"? Atbildēsim darba dienas laikā!
lv pcwp mitral stenosis|pcwp for pulmonary hypertension